CrowdSec WAF QuickStart for NGINX Ingress (Helm)
Objectives
This quickstart shows how to deploy the CrowdSec AppSec component with the official Helm chart and protect workloads exposed through the Kubernetes NGINX Ingress Controller. At the end you will have:
- CrowdSec running in-cluster with the AppSec API listening on
7422 - The ingress controller using the CrowdSec Lua plugin to forward requests for inspection
- Basic virtual patching rules blocking common web exploits
Pre-requisites
-
If you're new to the AppSec Component or Web Application Firewalls, start with the Introduction for a better understanding.
-
It's assumed that you have already installed CrowdSec Security Engine. For installation quickstart, refer to the QuickStart guide.
Deploy CrowdSec with AppSec enabled
Helm repository
Add or update the CrowdSec Helm repository:
helm repo add crowdsec https://crowdsecurity.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
Update CrowdSec configuration
Add this to the CrowdSec values.yaml with the AppSec configuration:
appsec
acquisitions:
- appsec_config: crowdsecurity/appsec-default
labels:
type: appsec
listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:7422
path: /
source: appsec
enabled: true
env:
- name: COLLECTIONS
value: crowdsecurity/appsec-virtual-patching crowdsecurity/appsec-generic-rules
This yaml configuration snippet exposes those important configuration items:
listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:7422exposes the AppSec API inside the cluster.- The two collections provide virtual patching and generic rule coverage.
- The chart bootstraps a bouncer named
nginx_ingress_wafusing the key you export locally.
And now we apply the new configuration with:
helm upgrade --install crowdsec crowdsec/crowdsec --namespace crowdsec --create-namespace -f crowdsec-appsec-values.yaml
Confirm the pods are healthy:
kubectl -n crowdsec get pods
You should see crowdsec-agent pods, the crowdsec-lapi pod and the crowdsec-appsec pod in Running state.
Enable the CrowdSec Lua plugin on NGINX Ingress
To extend the ingress controller with the CrowdSec plugin and point it to the
AppSec API, create the file named ingress-values.yaml. You can read the entire
file at crowdsec-docs/crowdsec-docs/docs/appsec/quickstart/nginx-ingress.mdx.
controller:
image:
registry: docker.io
image: crowdsecurity/controller
tag: v1.13.2
digest: sha256:4575be24781cad35f8e58437db6a3f492df2a3167fed2b6759a6ff0dc3488d56
extraVolumes:
- name: crowdsec-bouncer-plugin
emptyDir: {}
extraInitContainers:
- name: init-clone-crowdsec-bouncer
image: crowdsecurity/lua-bouncer-plugin:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: API_URL
value: "http://crowdsec-service.crowdsec.svc.cluster.local:8080"
- name: API_KEY
value: privateKey-foo
- name: BOUNCER_CONFIG
value: "/crowdsec/crowdsec-bouncer.conf"
- name: APPSEC_URL
value: "http://crowdsec-appsec-service.crowdsec.svc.cluster.local:7422"
- name: APPSEC_FAILURE_ACTION
value: "ban"
- name: APPSEC_CONNECT_TIMEOUT
value: "100"
- name: APPSEC_SEND_TIMEOUT
value: "100"
- name: APPSEC_PROCESS_TIMEOUT
value: "1000"
- name: ALWAYS_SEND_TO_APPSEC
value: "false"
command:
- sh
- -c
- |
sh /docker_start.sh
mkdir -p /lua_plugins/crowdsec/
cp -R /crowdsec/* /lua_plugins/crowdsec/
volumeMounts:
- name: crowdsec-bouncer-plugin
mountPath: /lua_plugins
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: crowdsec-bouncer-plugin
mountPath: /etc/nginx/lua/plugins/crowdsec
subPath: crowdsec
config:
plugins: "crowdsec"
lua-shared-dicts: "crowdsec_cache: 50m"
server-snippet: |
lua_ssl_trusted_certificate "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt"
resolver local=on ipv6=off;
API_URLtargets the Local API service exposed by the Helm chart.API_KEYdefines the key for the bouncer to be able to connect to CrowdSec LAPIAPPSEC_URLpoints to the AppSec service; keep the namespace in sync with your CrowdSec release.- The plugin copies the Lua files from the init container into an
emptyDirthat is mounted at runtime.
Deploy or upgrade the ingress controller with the new values:
helm upgrade --install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx \
--namespace ingress-nginx \
-f crowdsec-ingress-values.yaml
CrowdSec Ingress-NGINX Remediation Configuration Explained
This values.yaml snippet integrates the CrowdSec remediation (Lua bouncer)
into the ingress-nginx controller by injecting the Lua plugin, generating its
configuration, and enabling it inside NGINX.
Controller Image Override
controller:
image:
registry: docker.io
image: crowdsecurity/controller
tag: v1.13.2
digest: sha256:...
The controller image is replaced with a CrowdSec-enabled build that includes the required Lua integration points.
Shared Volume for the Plugin
extraVolumes:
- name: crowdsec-bouncer-plugin
emptyDir: {}
An emptyDir volume is used to hold the Lua bouncer plugin. It will be filled by an initContainer and mounted into the main controller.
InitContainer: Plugin Fetch and Configuration
extraInitContainers:
- name: init-clone-crowdsec-bouncer
image: crowdsecurity/lua-bouncer-plugin:latest
env:
- name: API_URL
value: "http://crowdsec-service.crowdsec.svc.cluster.local:8080"
- name: API_KEY
value: privateKey-foo
- name: BOUNCER_CONFIG
value: "/crowdsec/crowdsec-bouncer.conf"
- name: APPSEC_URL
value: "http://crowdsec-appsec-service.crowdsec.svc.cluster.local:7422"
- name: APPSEC_FAILURE_ACTION
value: "ban"
- name: APPSEC_CONNECT_TIMEOUT
value: "100"
- name: APPSEC_SEND_TIMEOUT
value: "100"
- name: APPSEC_PROCESS_TIMEOUT
value: "1000"
- name: ALWAYS_SEND_TO_APPSEC
value: "false"
command:
- sh
- -c
- |
sh /docker_start.sh
mkdir -p /lua_plugins/crowdsec/
cp -R /crowdsec/* /lua_plugins/crowdsec/
volumeMounts:
- name: crowdsec-bouncer-plugin
mountPath: /lua_plugins
The initContainer generates the plugin configuration (crowdsec-bouncer.conf) from environment variables and copies the Lua plugin files into the shared volume so the main controller can load them.
Mounting the Plugin in NGINX
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: crowdsec-bouncer-plugin
mountPath: /etc/nginx/lua/plugins/crowdsec
subPath: crowdsec
This mounts the plugin files inside the directory where ingress-nginx expects Lua plugins.
NGINX Configuration to Enable the Plugin
config:
plugins: "crowdsec"
lua-shared-dicts: "crowdsec_cache: 50m"
server-snippet: |
lua_ssl_trusted_certificate "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt"
resolver local=on ipv6=off;
This snippet enables the crowdsec Lua plugin, aAllocates shared memory for caching LAPI/AppSec results and ensures Lua HTTPS validation and DNS resolution work properly.
Summary
This configuration:
- Injects the CrowdSec Lua bouncer plugin into ingress-nginx.
- Generates its configuration via an initContainer.
- Mounts it into NGINX so it is executed during request processing.
- Enables both LAPI enforcement and optional AppSec forwarding depending on settings.
Testing the AppSec Component + Remediation Component
if you try to access http://localhost/.env from a browser, your request will be blocked, resulting in the display of the following HTML page:
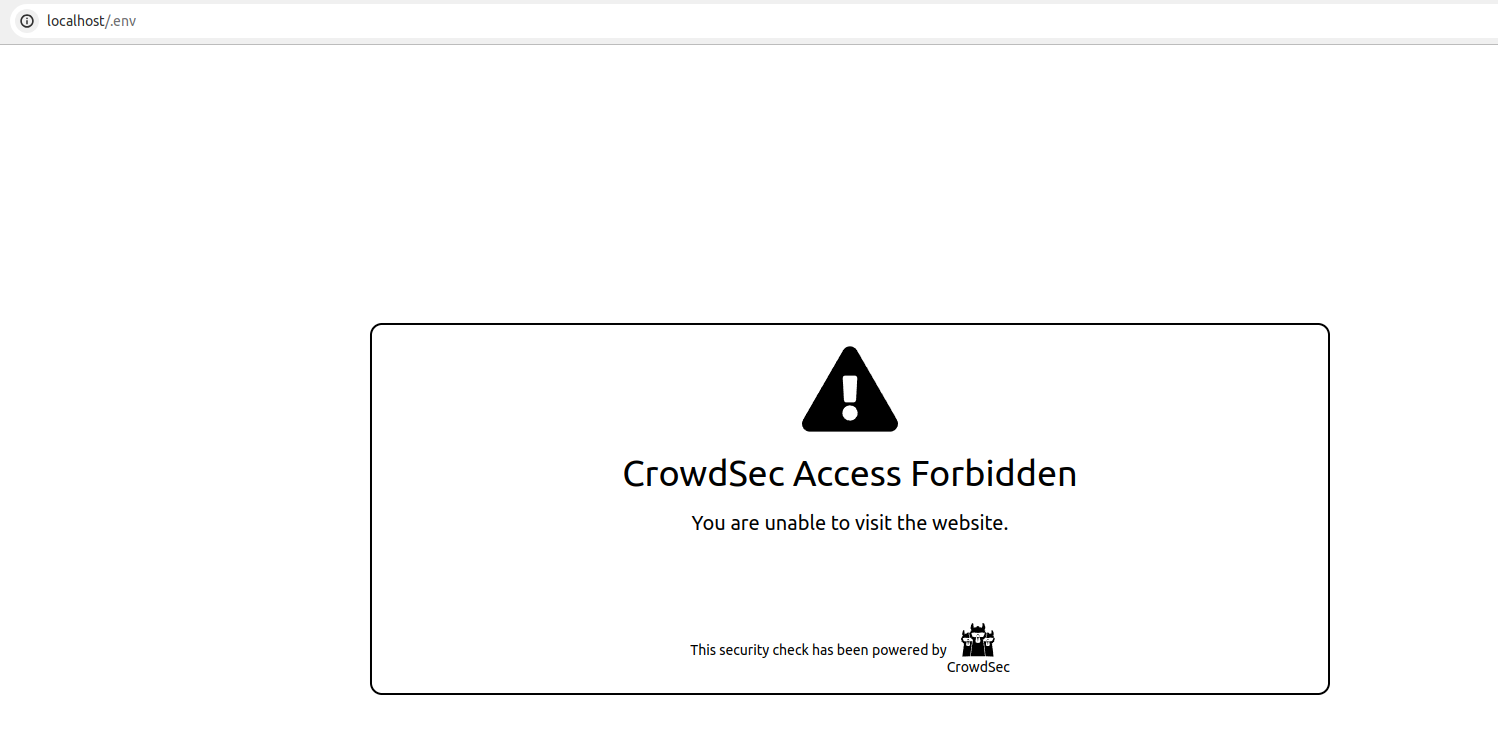
We can also look at the metrics from cscli metrics show appsec on the appsec pod it will display:
- the number of requests processed by the AppSec Component
- Individual rule matches
Example Output
Appsec Metrics:
╭─────────────────┬───────────┬─────────╮
│ Appsec Engine │ Processed │ Blocked │
├─────────────────┼───────────┼─────────┤
│ 127.0.0.1:7422/ │ 2 │ 1 │
╰─────────────────┴───────────┴─────────╯
Appsec '127.0.0.1:7422/' Rules Metrics:
╭─────────────────────────────────┬───────────╮
│ Rule ID │ Triggered │
├─────────────────────────────────┼───────────┤
│ crowdsecurity/vpatch-env-access │ 1 │
╰─────────────────────────────────┴───────────╯
You can test and investigate further with Stack Health-Check and Appsec Troubleshooting guide
Integration with the console
If you haven't yet, follow the guide about how to enroll your Security Engine in the console.
Once done, all your alerts, including the ones generated by the AppSec Component, are going to appear in the console:
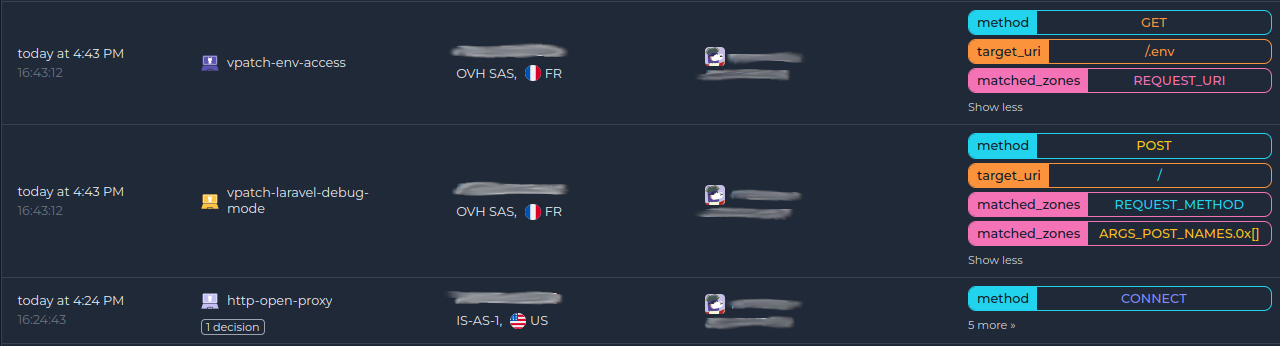
Next steps
You are now running the AppSec Component on your Crowdsec Security Engine, congrats!
As the next steps, you can:
- Explore the hub to find more rules for your use case
- Look at the Rules syntax and creation process to create your own and contribute
- Take a look at the benchmarks

